The greenhouse effect is one factor forcing global climate change;Seen in the response of the clearsky greenhouse effect 2 Methodology, Data, and Model 6 The clearsky greenhouse effect is defined as the difference between the surface emission and the clearsky outgoing longwave radiation (OLR) at the top of the atmosphere see Zhang and Sun, 06, equation (1) We Model simulations suggest that the observed effects are most pertinent to relatively small and shallow lakes, Uexpected greenhouse gas effect in lakes (19, September 9)
Rach Rob Pop Up Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Models Following A Geography Lesson On The Causes Of Climatechange For Year 8 A Task That Encourages Creativity And Aids Understanding Of
Greenhouse effect model
Greenhouse effect model-Greenhouse effect, then the implied climate sensitivity would be near the lower end of the accepted range of model predictions Natural variability ot the climate system could be as large as the changes observed to date but there are insufficient data to be ableGreenhouse Effect Teaching Box This teaching box provides resources related to the greenhouse effect It will help you teach how the greenhouse effect works, and how it prevents Earth from becoming a frozen ball of ice, and why there is too much of it happening today Teaching Boxes are collections of classroomready and standardsaligned




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
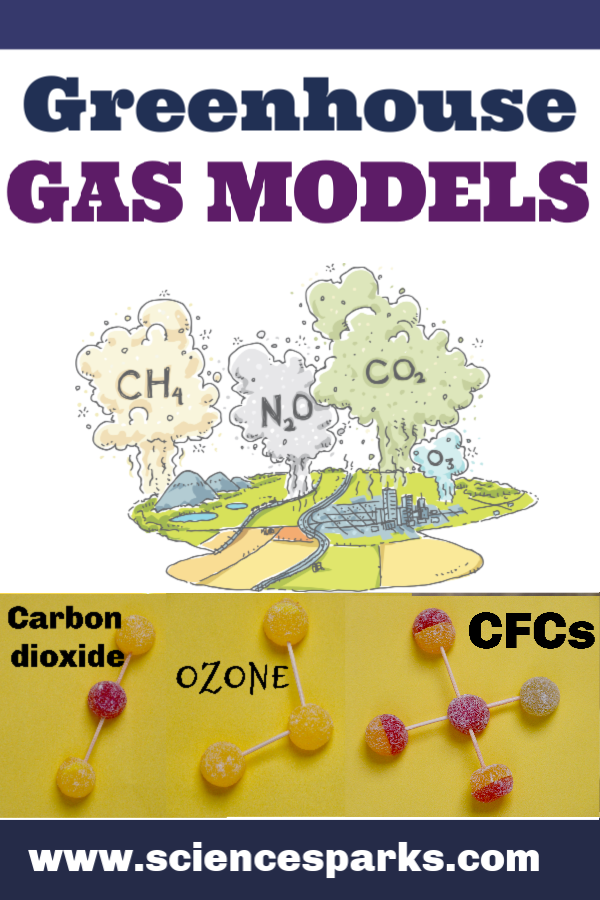
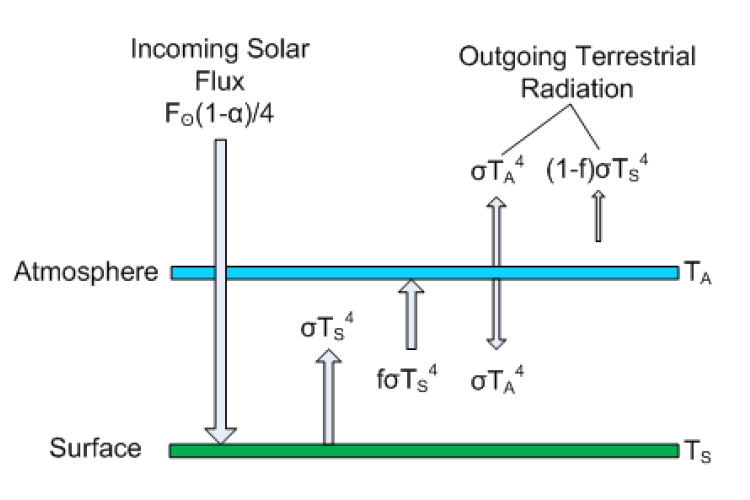
We can increase the complexity of the zerodimensional model by incorporating the atmospheric greenhouse effect in a slightly more realistic manner than is embodied by the ad hoc gray body model explored in the previous lecture We now include an explicit atmospheric layer in the model, which has the ability to absorb and emit infrared radiationThere seems to have been enough water to support abundant life, with sufficient land to reduce the planet's sensitivity to changes from incoming sunlightGreenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone, absorb and reemit longwave, infrared electromagnetic energy, thus trapping heat that warms the surface of the Earth This 6
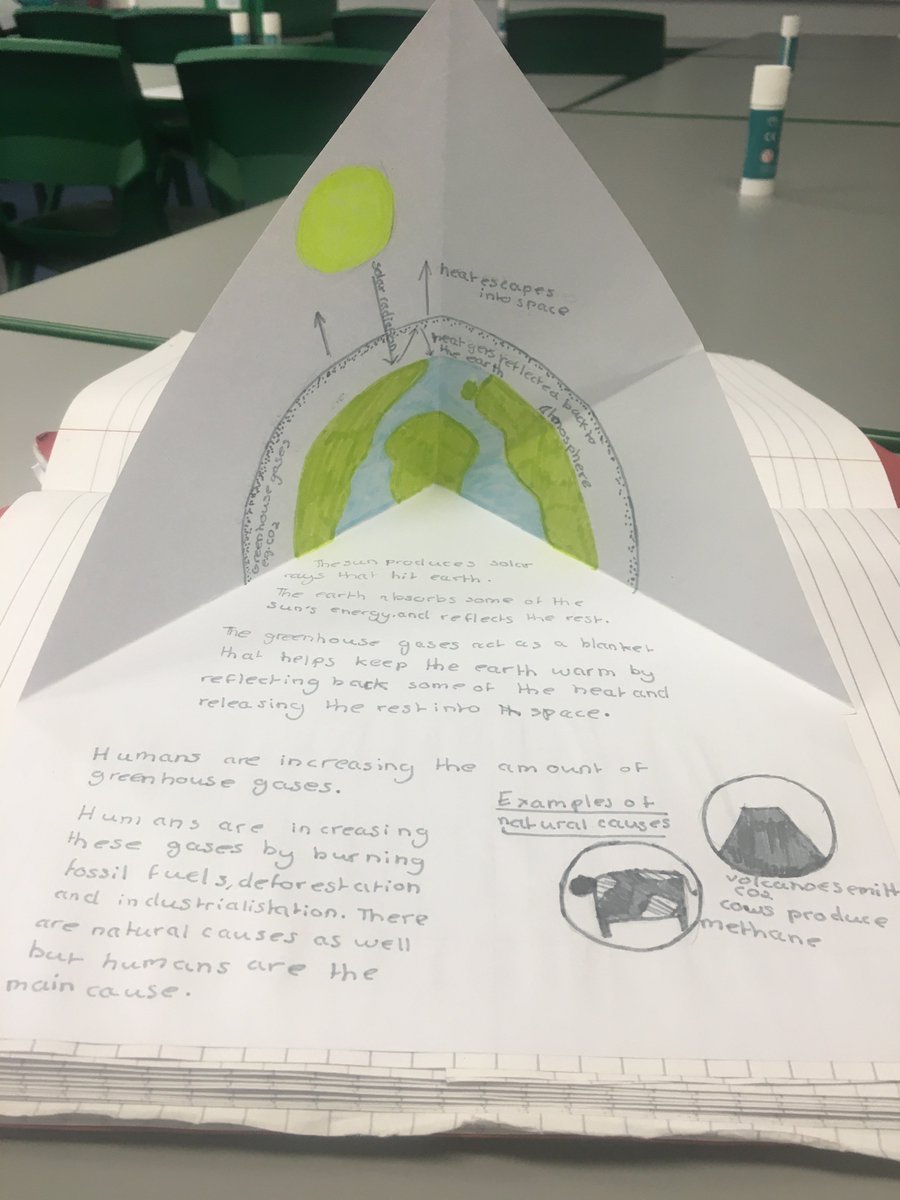
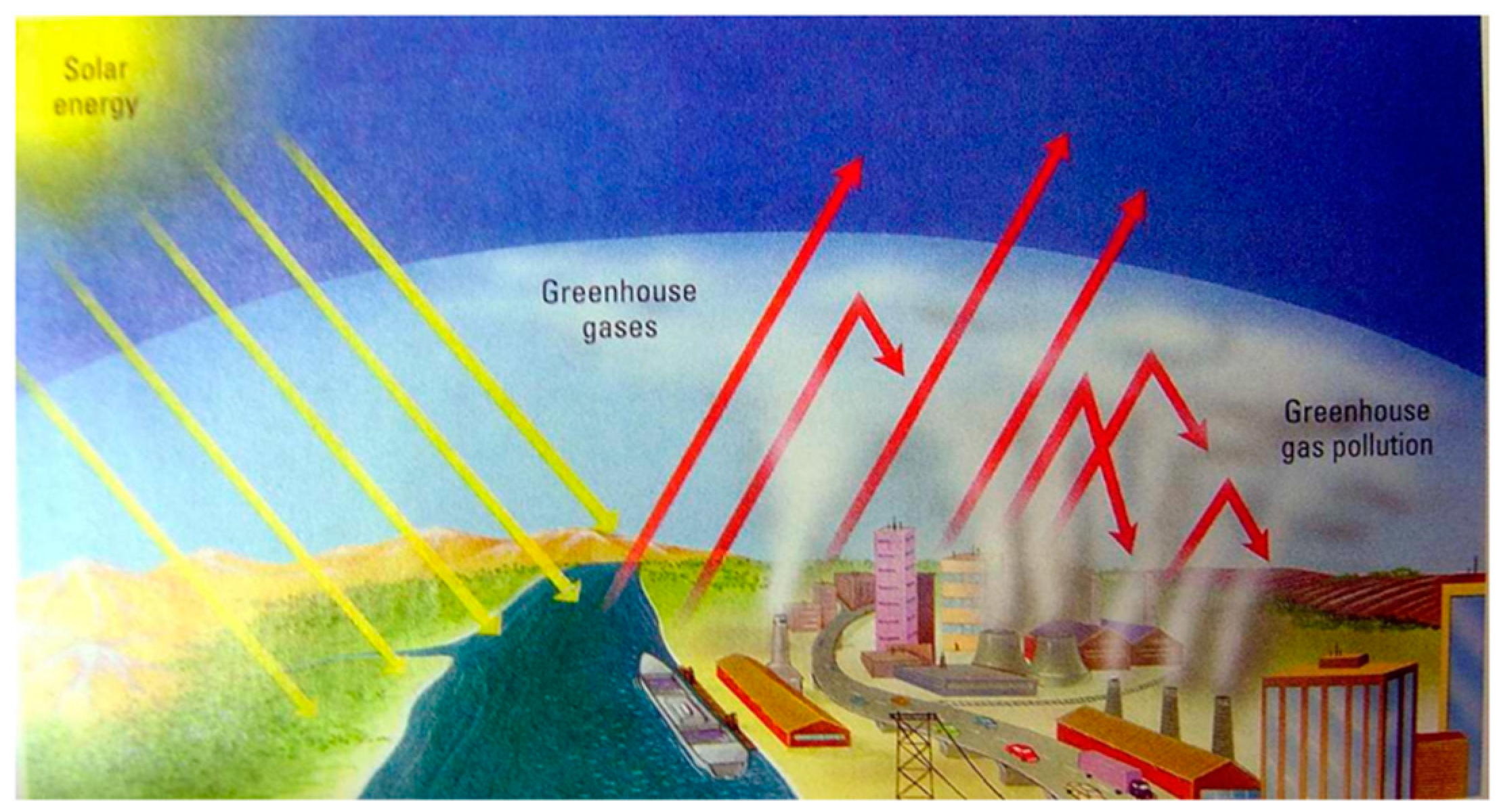
Global Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That is a great way for students to combine images and text in a creative way to produce quick and clear scientific diagrams Students are going to recreate a model of the greenhouse effect usingThe Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which the specific gases in the atmosphere of the Earth trap heat from the sun (see The Greenhouse Effect Diagram attachment) Typically, our atmosphere absorbs just the right amount of heat so that living things can survive Greenhouse effect is nothing but the process by which radiation from the planet's atmosphere warms up its surface to a temperature above the atmospheric level The thermal radiation from earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directions
Change the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes Then compare to the effect of glass panes Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?•Models represent reality in a simplified or idealized way • Used to understand or predict • Doesn't have to be realistic to be useful • GeneralizedHow do greenhouse gases affect the climate?




Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids



Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Gases CHAPTER 4 Why some gases are greenhouse gases, but most aren't, and some are stronger than others About Gases The layer model is what is called an idealization of the real world It has the essential ingredient of the greenhouse effect, but it is missing numerous things that are important in the real atmosphereThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouseThe Concept of Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity Let us rewrite the equation energy balance equation (3) above in a slightly different form,




Geo Expro Recent Advances In Climate Change Research Part Vi More On The Simple Greenhouse Model




27 Best Greenhouse Gases Ideas Greenhouse Gases Gas Greenhouse
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedAnother version of a greenhouse is what happens inside an automobile parked in the sun The sun's light and heat gets into the vehicle and is trapped inside, like the plastic bag around the jar The temperature inside a car can get over 1 degrees Fahrenheit (49 degrees Celsius) Download Project Add to collectionThe Layer Model Approximation to the Greenhouse Effect Download Earth Systems History III The Layer Model Approximation to the Greenhouse Effect Modified from a laboratory designed by Prof David Archer, Professor, University of Chicago and author of the book Global Warming Understanding the Forecast




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
Observe the Greenhouse Effect in a Jar This experiment gets kids exploring how a greenhouse works, and in turn how greenhouse gases affect the Earth's atmosphere Your child will strengthen observation and recording skills, work with a control, and draw conclusions And bonus this is a great outdoor activity!The greenhouse gases most responsible are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide In this experiment, you will use two Temperature Probes to measure and compare the temperatures in model greenhouses under various conditions In Part I, you will investigate the role of a plastic covering over the top of the model greenhouseGreenhouse effect The radiation budget of the atmosphere is reviewed, and a simple balanced model is designed permitting the calculation of a mean surface and a mean atmospheric temperature The increased greenhouse effect is simulated by the model Various calculations



2




Molecular Model Methane Greenhouse Effect Gas Print
After viewing greenhouse effect PowerPoint slides, students will correctly order 4 of 6 steps in the greenhouse effect and identify 4 of 6 greenhouse gasses 2 Through a greenhouse effect drama, students will demonstrate their knowledge of the greenhouse effect by playing their roles correctly during the drama 3Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today What happens when you add clouds?4 The Layer Model Sco Denning CSU CMMAP ATS 1 The Layer Model of the Greenhouse Effect ATS 150 Lecture 4 Please read Chapter 3 in Archer Textbook What is a Model?




Howtofunda Global Warming Effects Greenhouse Project Model For School Science Exhibition Facebook



Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids
That limits the amount of water evaporated from the oceans and, as a result, the greenhouse effect by water vapor This type of surface appears ideal for making a planet habitable;Lecture 6 Greenhouse Effect, Habitability Overview A simple model of the overall Earth's heat budget is derived The Earth is assumed to be in equilibrium with the input of solar radiation balanced by the output of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface Students read to create an initial conceptual model of the greenhouse effect They then collect temperature data from a physical demonstration simulating atmospheres with and without greenhouse gases and calculate and compare the mean, median, and range Finally, they revise their model of the greenhouse effect using their data analysis and an




Global Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That Is A Great Way For Students To Combine Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
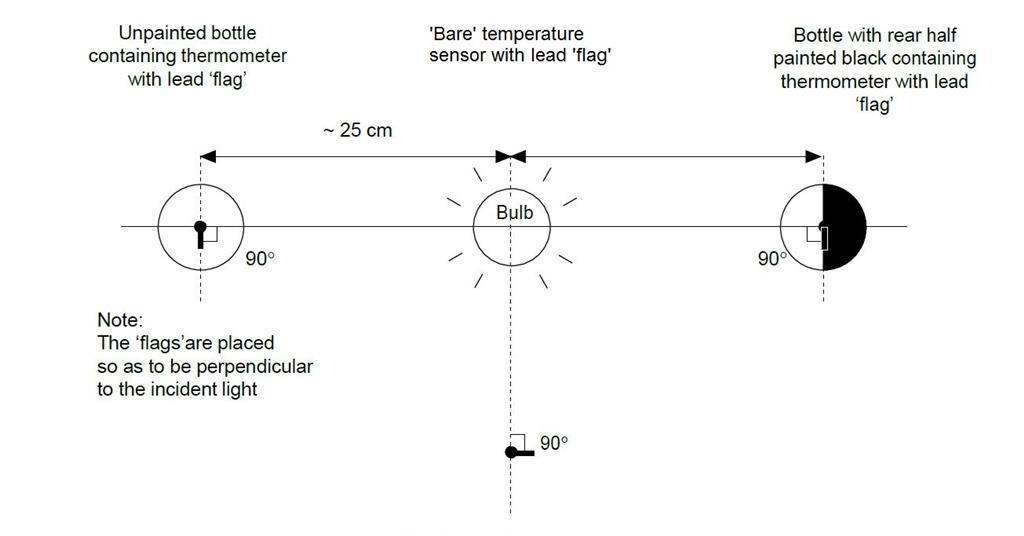
The Greenhouse Effect Model Set up your greenhouse model as follows 1 In both bottles, place a small layer of dirt or gravel in the bottom to simulate the surface of the earth 2 Tape a piece of cardboard to the back of each thermometer, to shield it from the direct light ofGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effectIn other words, the greenhouse effect has the effect of warming Earth from a frigid average temperature of 18 o C to a far more hospitable 15 o C!




Greenhouse Gases Molecular Models Stock Image C028 0986 Science Photo Library




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
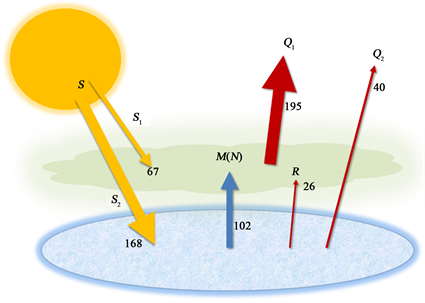
The model used to determine the Greenhouse Effect took the incoming Solar constant of 1370 Watts per square metre and spread that across the whole spherical surface of the Earth, that is, 3425 W/m^2, as the average irradiance Using an albedo of 03, this gives theGreenhouse effect and "enhanced" greenhouse effect OUR HYPOTHESIS At the end of this activity, we hypothesize that the "enhanced" greenhouse effect environment will be 4*C warmer than the greenhouse effect environment at the end of a minute observation Materials 2 empty plastic water bottlesFirst Climate Model The balance of energy flow, as incoming sunlight and outgoing infrared, allow us to create our first simple climate model, including a simple greenhouse effect There are two extended exercises in Part II of this class, one an analytical (algebraic) model of the equilibrium temperature of a planet, the other a numerical




Rach Rob Pop Up Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Models Following A Geography Lesson On The Causes Of Climatechange For Year 8 A Task That Encourages Creativity And Aids Understanding Of



1
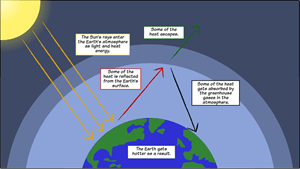
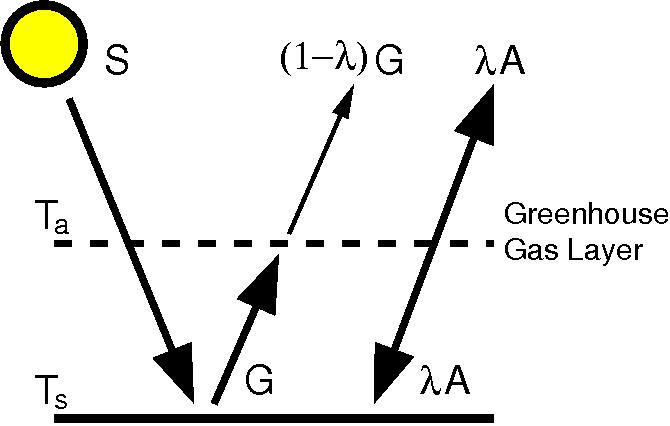
OSTIGOV Technical Report Simple model of the greenhouse effect Simple model of the greenhouse effect Full Record;The greenhouse effect can be illustrated with an idealized planet This is a common "textbook model" the planet will have a constant surface temperature T s and an atmosphere with constant temperature T a For diagrammatic clarity, a gap can be depicted between the The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides




Greenhouse Effect



Education Sciences Free Full Text Visualizing The Greenhouse Effect Restructuring Mental Models Of Climate Change Through A Guided Online Simulation Html
Australian scientists are working on many aspects of the greenhouse effect Some scientists try to determine climatic trends, or model the effect of the enhanced greenhouse effect on Australia's climate and economy Others work on the Antarctic ice cap, to see what impact the enhanced greenhouse effect may be having thereThe greenhouse effect is the process in which the emission of infrared radiation by the atmosphere warms a planet's surface The name comes from an analogy with the warming ofThe greenhouse effect, despite all the controversy that surrounds the term, is actually one of the most wellestablished theories in atmospheric science For example, with its dense CO2 atmosphere, Venus has temperatures near 700 K at its surface Mars, with its very thin CO2 atmosphere, has temperatures of only 2 K




Global Warming School Science Exhibition Models Diy School Project Working And Non Working Models For Science Exhibitions Or Science Fair




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
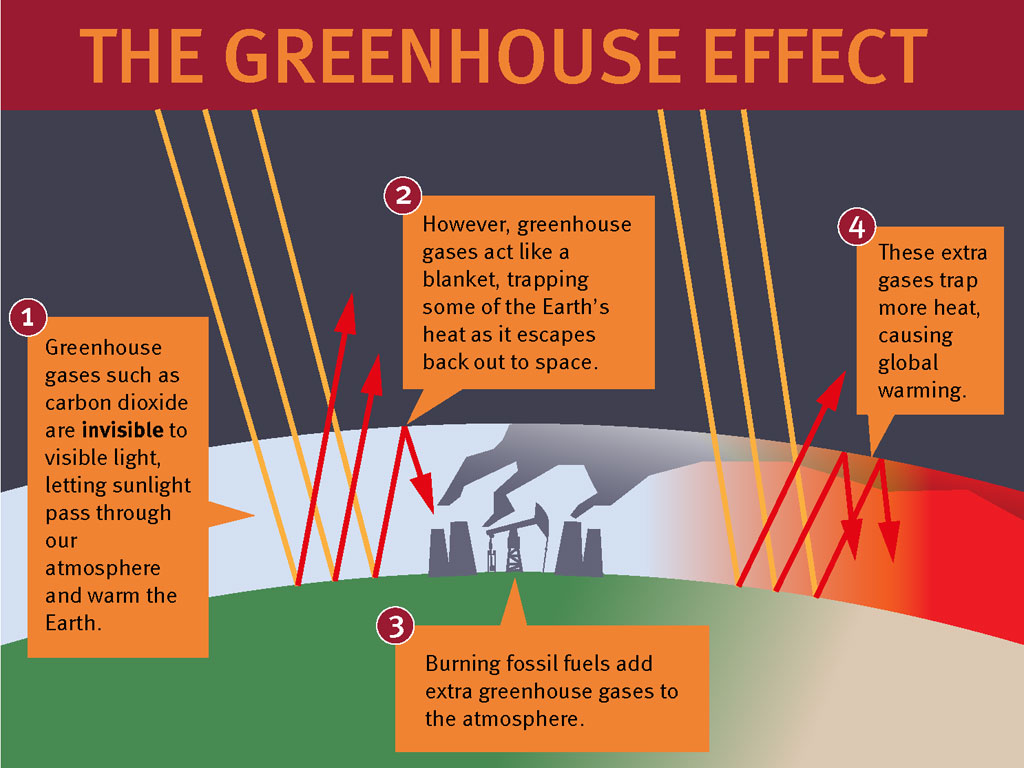
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinated gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat thatVapour in the air that the greenhouse effect is very large, adding a small additional amount of CO 2 or water vapour has only a small direct impact on downward infrared radiation However, in the cold, dry polar regions, the effect of a small increase in CO 2 or FAQ 13, Figure 1 An idealised model of the natural greenhouse effect See To address global warming, engineers of all disciplines must understand the greenhouse effect and its causes, and then creatively design new technologies to reduce the production of greenhouse gases Some engineers examine the types of chemicals released in the manufacturing process, and redesign new ways of production or methods to remove harmful




Policy Analysis Of The Greenhouse Effect Model Deconstructingrisk



Realclimate Learning From A Simple Model
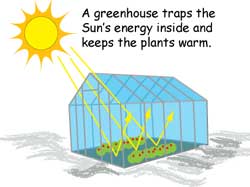
In this lab, students measure temperature changes inside soda bottles (one with CO2 added, the other with only air inside) as incandescent light is shined on them to model the Greenhouse Effect Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warm Even in the winter, with no heat source but the Sun on a clear day, a greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside In the summer, if a greenhouse gets too hot, the gardener can open the windows and doors and maybe turn on a fan



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




An Idealized Model Of The Natural Greenhouse Effect Source Ipcc Wg1 Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Model School Project For Students Exhibition Models The4pillars Youtube




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Studying And Projecting Climate Change With Earth System Models Learn Science At Scitable




Identify What Happens To Light In This Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Brainly Com




Greenhouse Effect Ideas Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Earth Science




Modeling The Greenhouse Effect Experiment Ngss Aligned Stem Tpt




An Idealized Model Of The Natural Greenhouse Effect Source Ipcc Wg1 Download Scientific Diagram




Global Warming Cartoon Png Download 1332 1661 Free Transparent Global Warming Png Download Cleanpng Kisspng




Pdf On The Numerical Exploration Of Zero Dimensional Greenhouse Model Using Newton Raphson And Steepest Descent Methods Semantic Scholar



The Greenhouse Effect Storyboard By Oliversmith



Modelling The Greenhouse Effect Experiment Rsc Education




The Greenhouse Effect By Mig26 On Deviantart




Model Of Green House And It S Effects Youtube




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia Republished Wiki 2



Greenhouse Effect




Ppt The Layer Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Powerpoint Presentation Id




Identify What Happens To Light In This Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Brainly Com




Dirike Model Based Learning And Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Rach Rob Pop Up Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Models Following A Geography Lesson On The Causes Of Climatechange For Year 8 A Task That Encourages Creativity And Aids Understanding Of




Climate Change Education In Vanuatu 1 Background Information



Joseph Postma And The Greenhouse Effect




Natural Greenhouse Effect 5 The Standard Gh Model Where The Download Scientific Diagram



The Idealised Greenhouse Effect Model And Its Enemies Scienceblogs



Global Warming Images



Greenhouse Effect Simcenter




Chapter 6 The Greenhouse Effect And Climate Feedbacks Ppt Video Online Download




Greenhouse Effect Model Science Exhibition Project Diy School Fair Project Youtube




About Greenhouse Effect Responsible Model With Tights On Face Wearing Plastic Clothing Speaking About Greenhouse Effect Stock Photo Alamy




Greenhouse Effect Model Explained In English Howtofunda Youtube




Simple Model Of The Greenhouse Effect Includes Atmosphere Layer Atmosphere Layer Passes All Solar Radiation Atmosphere Layer Absorbs All Ir From Earth Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect Article Model With Tights On Face Lying On Floor Posing For Greenhouse Effect Article Stock Photo Alamy




Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustrations 3 213 Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Air Pollution And Its Environmental Effects Bellringers 927




Greenhouse Effect Illustration Stock Photo By C Casaltamoiola




Greenhouse Effect Model Science Exhibition Project Green House Effect Model School Project Youtube




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect Game Kids Against Climate Change



2



Atmosphere Layers Greenhouse Effect Model Activity Mosaic Expedition



Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Download Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Png Images Free Cliparts On Clipart Library




National Academies And The Non Greenhouse Gas Effect Part 5 Johnosullivan



The Greenhouse Hypothesis Page 2



Interactive Greenhouse Effect 3d Model By Visartech Visartech 6c6bf49




Greenhouse Effect Model Efecto Invernadero Dieta Balanceada



Simple Time Dependent Model Of The Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Roy Spencer Phd




Greenhouse Effect Model Explained In English Howtofunda Youtube



Greenhouse Effect




Young Model Posing For Campaign About Greenhouse Effect Stock Image Image Of Problem Model




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




Greenhouse Effect




The Idealised Greenhouse Effect Model And Its Enemies Wmconnolley Scienceblogs Com Stoat Archive



The Greenhouse Effect An Evaluation Of Arrhenius Thesis And A New Energy Equilibrium Model



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Ideas 30 Of Greenhouse Effect Model 3d Indexofmp3fantasy
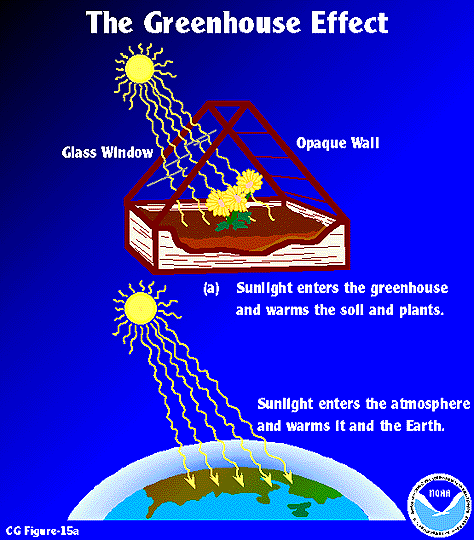



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa



2




Idealized Greenhouse Model Wikipedia



If We Continue Releasing Greenhouse Gases We Are Going To See Global Warming So What Are The Maximum Negative Effects That We Will See Quora




Ipcc Explains The Greenhouse Effect Climate Audit



1




Sbhsgeography Another Greenhouse Effect Model Geography




Howtofunda Greenhouse Effect Model Facebook




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education



File Greenhouse Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons




Low Poly Sci Fi Greenhouse 3d Model 3dhunt Co
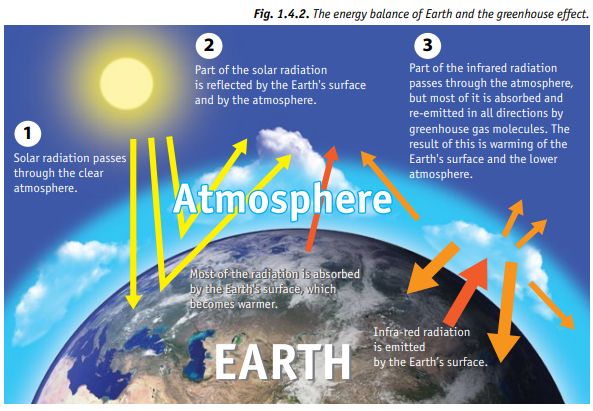



1 4 Climate Change Today Undp Climate Box



3




2d Greenhouse Gas Lab




Image Definition Integrated Model For Assessment Of The Greenhouse Effect Abbreviation Finder




Working Model On Global Warming And Green House Effect
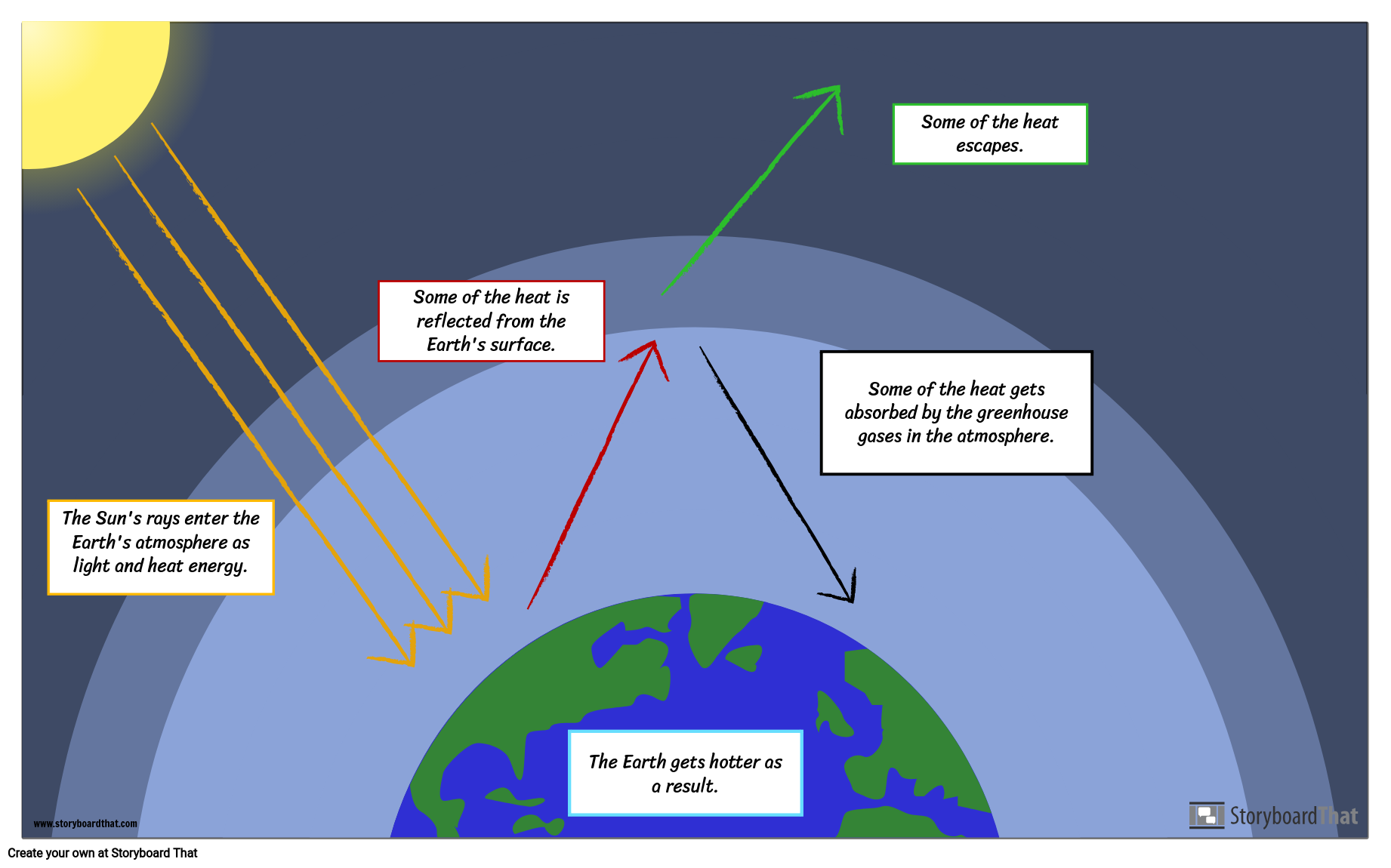



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering



Richard Harwood S Courses Physical Geography 101 Greenhouse Effect




Image An Integrated Model To Assess The Greenhouse Effect Springerlink



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿